Accelerators
-
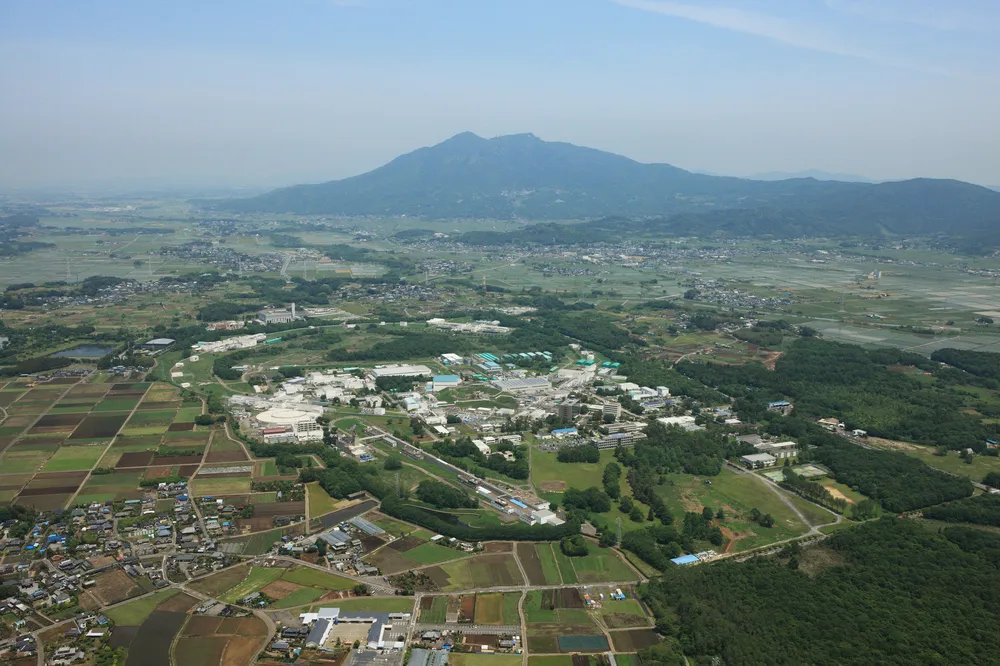

SuperKEKB
The SuperKEKB project is our response to the challenge of solving Nature’s fundamental puzzles by upgrading the KEKB electron-positron collider and the Belle detector. The KEKB accelerator and the Belle detector demonstrated the violation of CP asymmetry proposed by Dr. Makoto Kobayashi and Dr. Toshihide Maskawa, who received the 2008 Nobel Prize in Physics. The…
-

PEP II
The experimental physics program using the SLC started with the MarkII detector in 1989, which demonstrated that same year the first evidence that only three families of matter particles exist. The Stanford Linear Collider was a linear accelerator that collided electrons and positrons at SLAC. Its construction began in 1983 and was completed in 1987.…
-
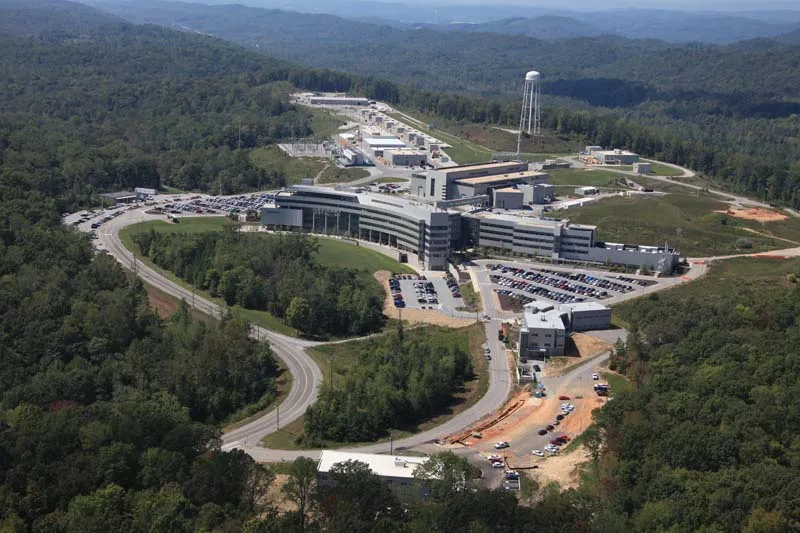

Spallation Neutron Source
SNS is an accelerator-based neutron source in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. facility provides one of the most intense pulsed neutron beams in the world for scientific research and industrial development. The construction of SNS was a partnership of six DOE national laboratories: Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Los Alamos, Oak Ridge, and Jefferson. It was completed…
-

Tevatron
The Tevatron is a circular particle accelerator in the United States, at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (also known as Fermilab), just east of Batavia, Illinois. The 6.86 km circumference ring contains two detectors: CDF for Collider Detector at Fermilab and DZero. In 1995 CDF and DZero experiments announced discovery of the top quark. The…
-
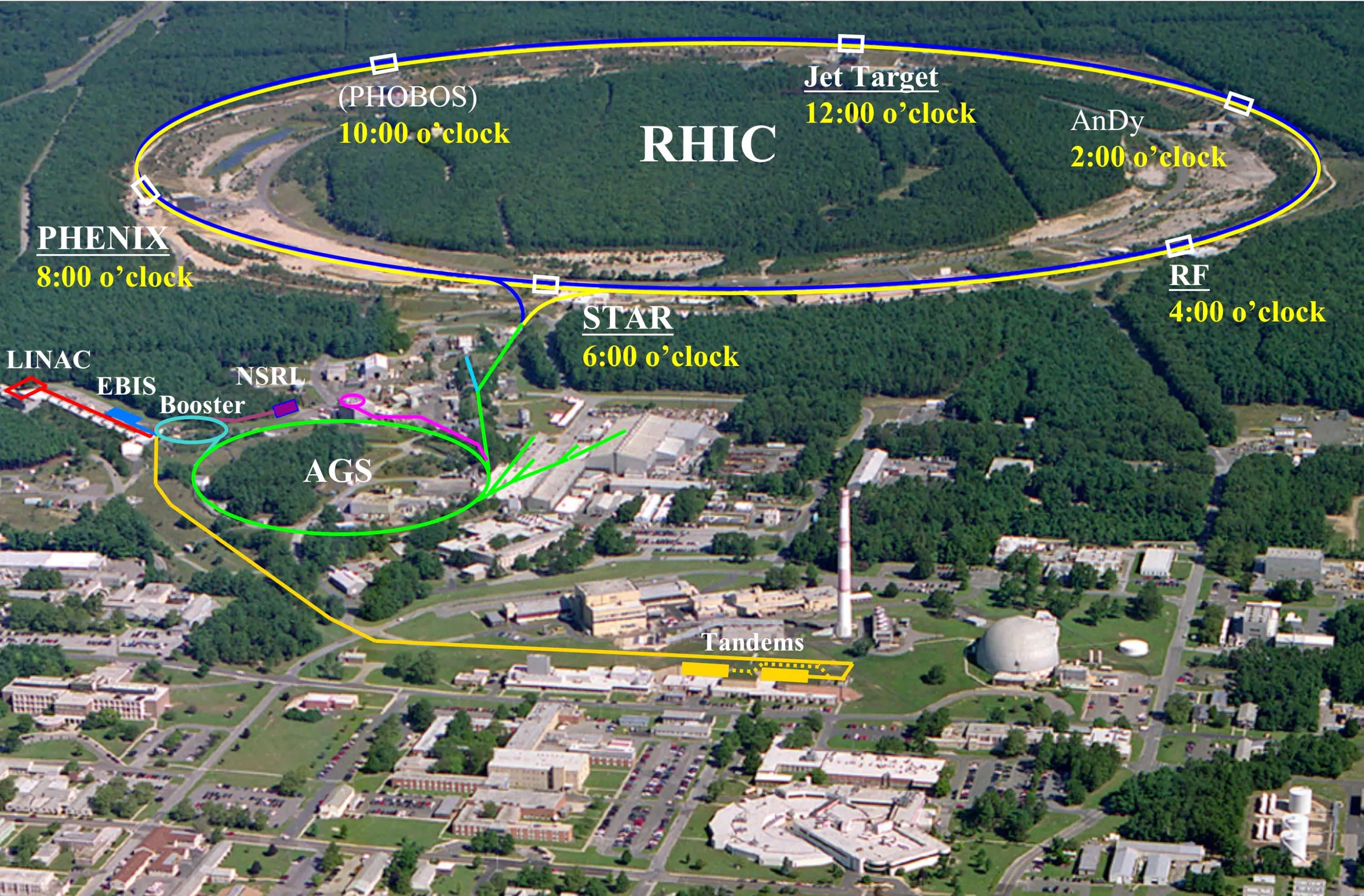
Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC)
The RHIC is a heavy-ion and spin-polarized proton collider. It is located at Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) in Upton, New-York and was started up in 2000. RHIC’s double storage ring is itself hexagonally shaped and 3834 m long in circumference, with curved edges in which stored particles are deflected and focused by 1,740 superconducting magnets.…
-

HERA
(Hadron Elektron Ring Anlage) was a 6.3-kilometer-cirumference proton-electron collider at DESY, Hamburg, Germany. The storage ring started in 1992 and joined the effort of 11 countries. HERA had four huge detectors and associated experiments H1, ZEUS, HERMES and HERA-B. The experiments were dismantled in 2007 HERA-B detector stopped taking data in 2003.
-
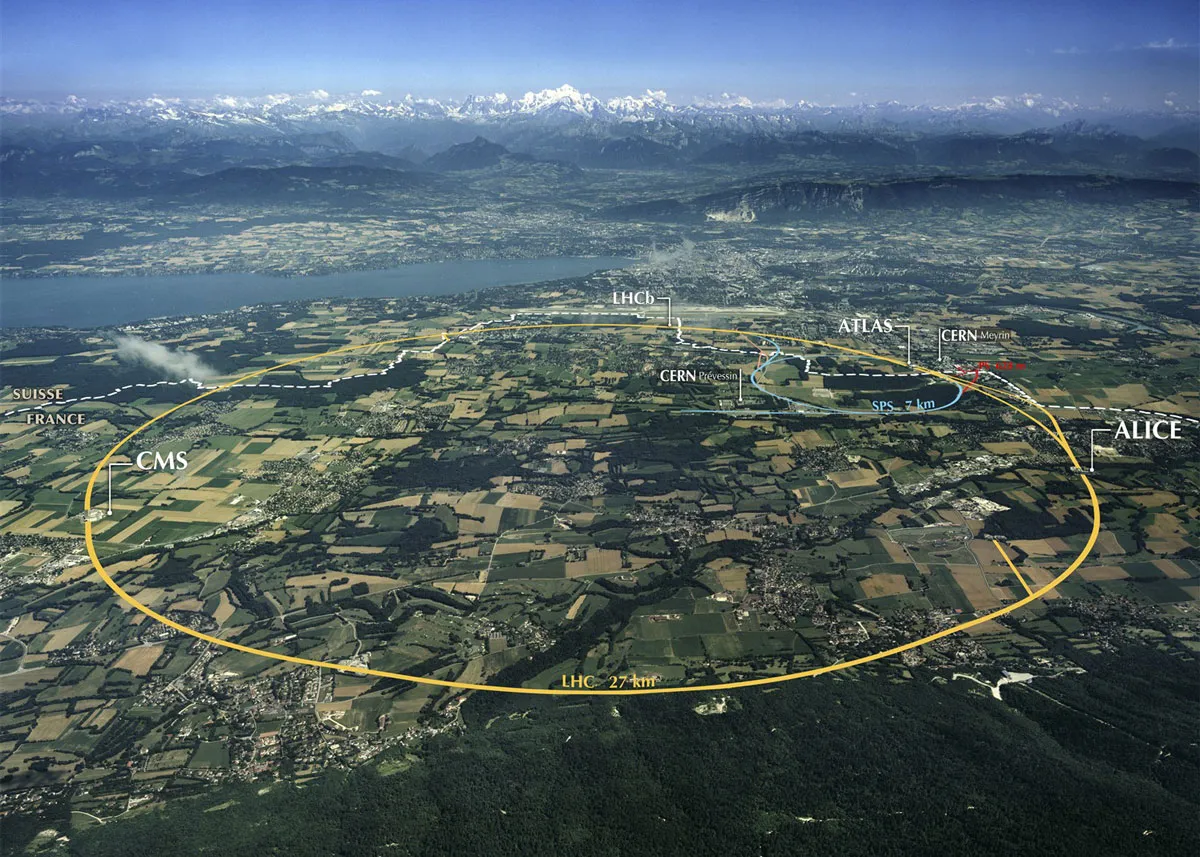

Large Hadron Collider (LHC)
The LHC consists of a 27-kilometre ring of superconducting magnets with a number of accelerating structures to boost the energy of the particles along the way. Further information can be found here: http://home.cern/topics/large-hadron-collider ATLAS, CMS, ALICE and LHCb are LHC’s four main detectors. Three smaller detectors also exist in the LHC and are used for…
-
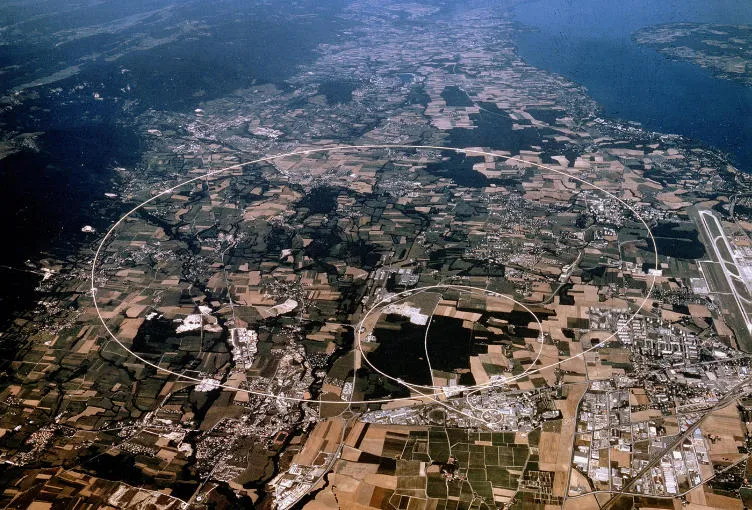

Large Electron Positron collider (LEP)
The Large Electron-Positron collider (LEP), was a 27-kilometre-circumference electron-positron accelerator. Its construction started in 1983 after the inauguration on 13 September, and the first beam circulated on 14 July 1989. More information can be found here: https://home.cern/about/accelerators/large-electron-positron-collider Four detectors : Apparatus for LEP PHysics (ALEPH); DEtector with Lepton, Photon and Hadron Identification (DELPHI); L3 and…
